Polymer nanowires remain conductive after lithography-free manufacturing enabling an excellent path for intracellular bioelectronic manipulation of stem cells and algae. A new study spearheaded by NanoLundians Damien Hughes and Martin Hjort presents a simple, yet efficient way to bring conductive polymers into a nanowire shape suitable to interface with living cells – and even allowing them to get really cozy together!
Making conductive polymer nanowires to probe cells
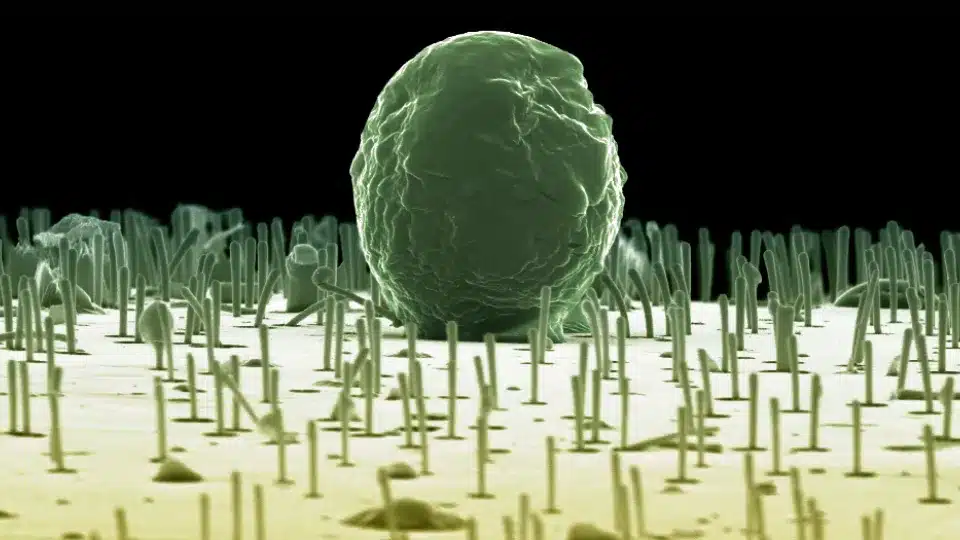
Electron microscopy image of algae sitting on the nanowires. Picture: Martin Hjort