New process offers extreme precision that could revolutionize medical diagnostics and beyond.
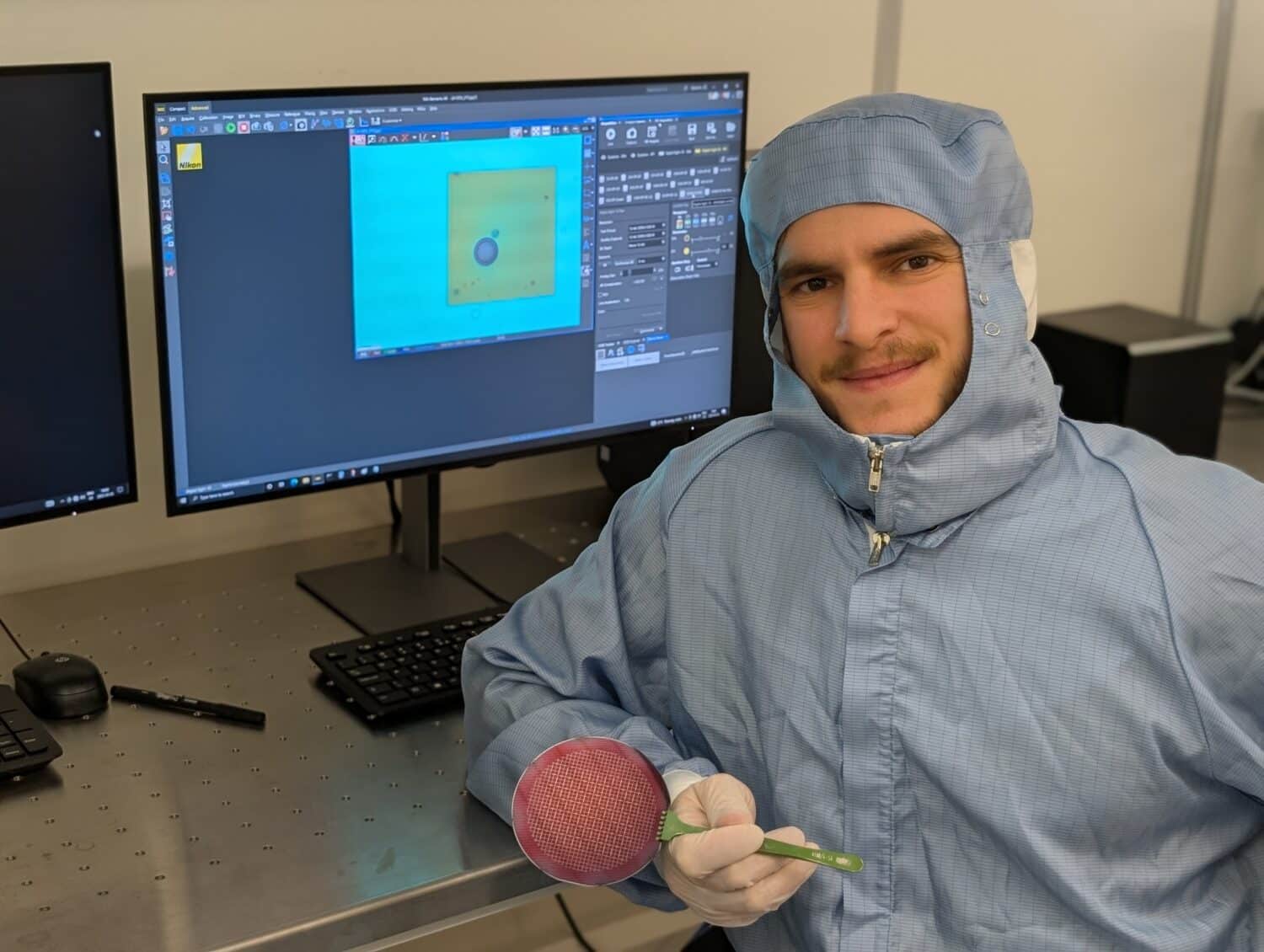
KTH PhD student Fabio De Ferrari and colleagues have discovered a cost-effective way to create ultra-small pores in silicon – smaller than 5 nanometers in diameter.
Using gold nanoparticles and a method called metal-assisted chemical etching, the researchers also discovered a self-limiting effect—like a drill that stops automatically at just the right depth—making the technique highly precise and scalable.