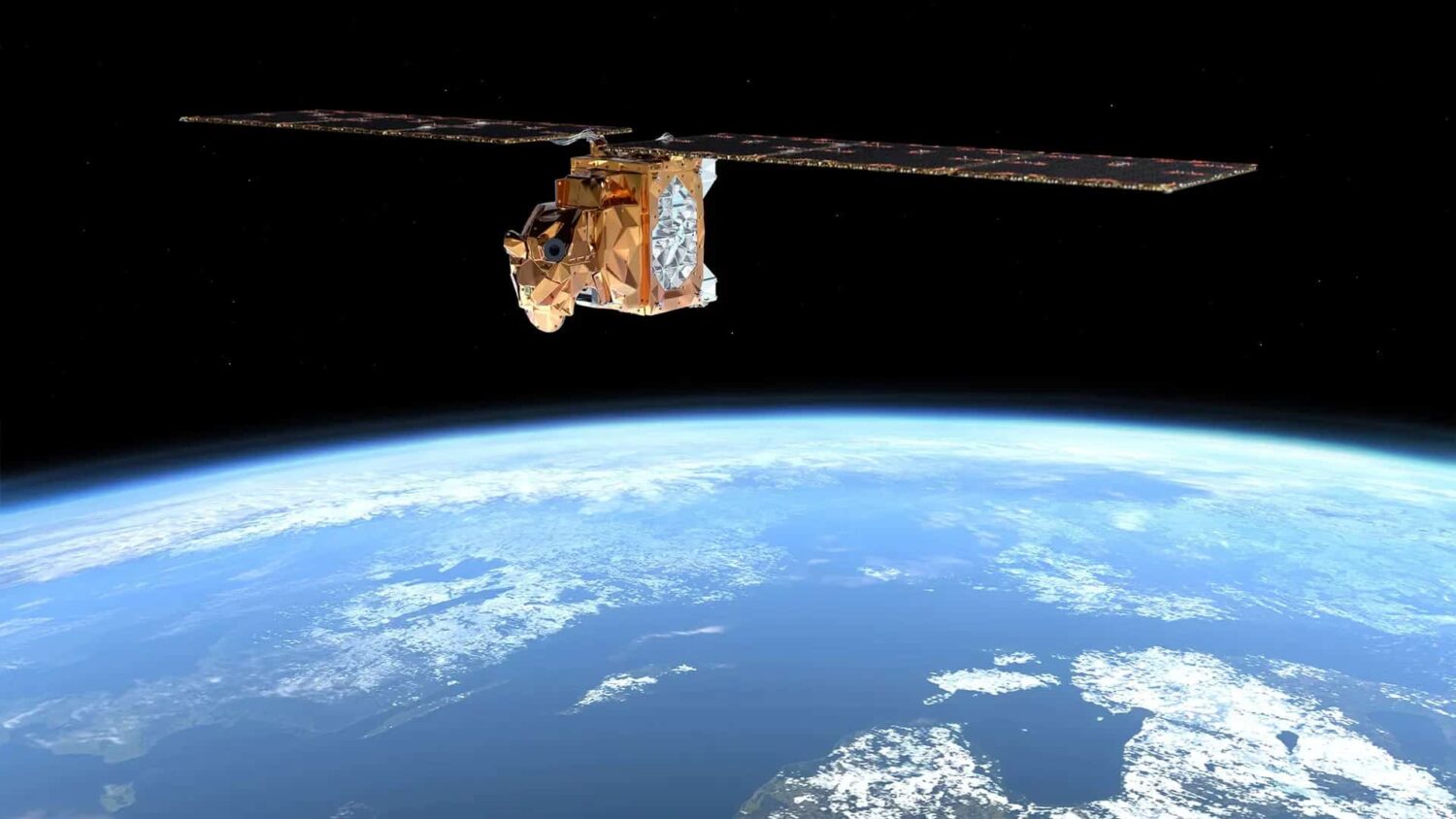
With only 125 kilos in weight – and as small as the size of a dishwasher – the first Arctic Weather Satellite, AWS, has successfully been launched with the mission to provide better weather forecasts for the Arctics, a region severely affected by climate change. The small satellite is equipped with a 19-channel cross-track microwave radiometer using semi-conductor technology fabricated at Chalmers University of Technology.
The new Arctic weather satellite, AWS, was lofted into orbit on 16 August at 20:56 CEST aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, just north of Los Angeles. About six hours later, the KSAT ground station in Svalbard, Norway, received the all-important signal indicating the satellite’s safe arrival in orbit.
With a mission to collect important data on moisture and temperature levels in the Earth’s atmosphere, and measure the amount of ice in clouds, the satellite is sent off to enhance our understanding of the weather conditions at the poles. The clouds, and what happens inside them, are important parameters when trying to predict climate change.